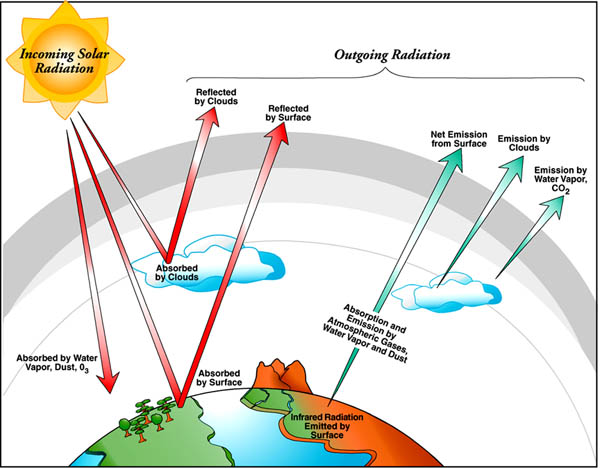
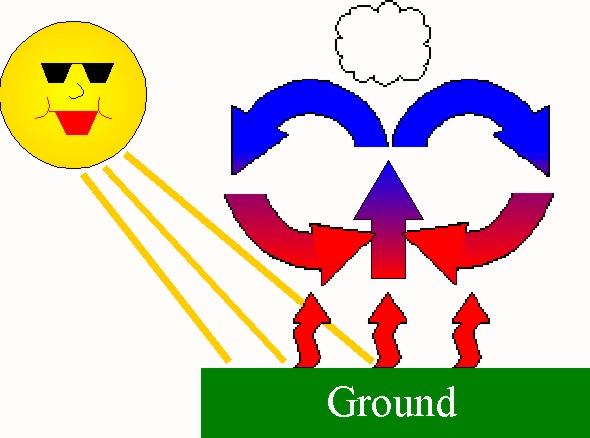
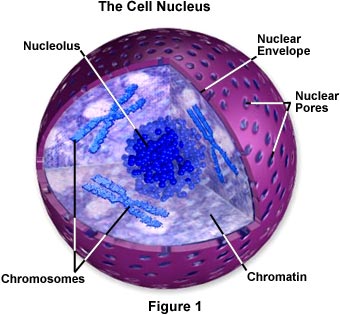
biomass conversion getting energy from plant and animal materials by changing them into high-quality fuels

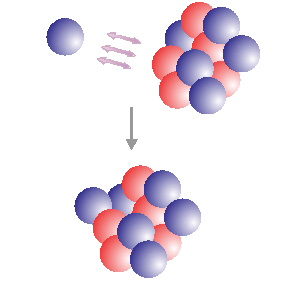
nuclear fission the spliting of a nucleus with large mass into two nuclei with smaller masses

chain reaction a reaction that kept going by prducts of reaction

nuclear fiction the merge of nuclie with smaller masses into a nucleus with a larger mass

hydroelectricity the use of flowing water to generate elctricity

thermal pollution the excess of the enviroment